Decision Optimization Center for Planning and scheduling challenges
Developing a realistic plan or schedule that provides the best possible balance between customer service and revenue goals is hard work. While optimization technology has long been used to find the best solutions to complex planning and scheduling problems, an application environment that supports the flexible exploration of all trade-offs and sensitivities is often missing.
- Plans are out of date as soon as they are created
- No matter how prepared we are, each planning cycle is affected by future uncertainties – prices, demand, supply, weather effects, …
- we don’t have a clear vision of possible future scenarios and their effect on plans
- we get caught in a costly reactive cycle where we fix issues after the fact, instaed of anticipating and planning for them.
What business people need
- flexibility to develop and compare realistic planning and scheduling scenarios
- quality sensitivity analysis and explanations
- collaborative planning and scenario sharing
- decision recommendations powered by the world’s leading optimization engines
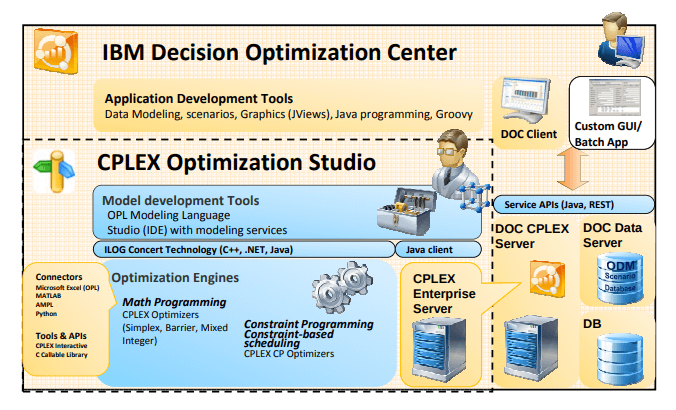
Overview: IBM Decision Optimization Center (DOC)
IBM Decision Optimization Center (DOC)is a solution platform for optimized decision, planning and scheduling solutions. Previously known as Optimization Decision Manager (or ODM Enterprise). There are 6 editions.
(D) IBM Decision Optimization Center Developer Edition
- a complete optimization app IDE based on the Eclipse Framework + CPLEX (OPL, CPLEX Optimizers, CPO) + DOC + OS + DS
- for both optimization expert and software developer
- Java customization (custom GUI, data import/export, …)
- ILOG JViews Enterprise (custom visualization)
- pre-installed and pre-configured WAS
(OS) IBM Decision Optimization Center Optimization Server
- a centralized, server-based implementation of the CPLEX and CPO engines.
- Deployment to serve remote solve requests
- required for solving (or resolving) of optimization models or execution of algorithms to support decisions by planners using the DOC Client (C) in an enterprise configuration (multiple users sharing scenarios and solving remotely)
- CPLEX Enterprise Server (CES): a separately licensed component of CPLEX Studio, provides the capability to deploy DO apps in the enterprise environments using a client-server architecture.
- CPLEX as a network service
- Job management including Fail-over
- Scalable & robust
- OPL models only
- Less integration effort than embedding CPLEX in every application
- Includes IBM WebSphere Application Server (WAS) for Developers 8.5.5* (cannot be used for deployment)
(OE) IBM Decision Optimization Center Optimization Engine
- local desktop implementation of CPLEX and CPO engines.
- Deployment to serve local solve requests
- DOC Planner (P) in Individual configuration (single users not sharing scenarios concurrently and solving/resolving locally)
- DOC Client (C) in an enterprise with local optimization configuration: multi-user mode, with users sharing scenarios using (DS) but solving locally
(DS) IBM Decision Optimization Center Data Server
- a centralized, server-based collection of services intended to facilitate data management for DOC apps.
- Deployment to serve remote scenario management
- provides a portal between DOC Client and the ODM Scenario Repository database.
- Scenario Management: Manages the Scenario Repository
- REST API (e.g. web UI)
- can be connected to (OS)
- required for all deployment configurations that use DOC Client for (OE) locally or (OS) remotely
- Includes WAS for Developers* (cannot be used for deployment)
(C) IBM Decision Optimization Center Client Edition
- provides a Studio (business UI)
- a run time component that allows users to view, solve, share and interact with distributed DOC apps.
- configurable & customizable views (pivot, 2d, charts, …)
- collaborative planning
- what-if analysis
- Scenario creation/edition/modifications via (DS)
- Submit of solve requests to remote (OS) or (OE) locally
(P) IBM Decision Optimization Center Planner Edition
- same functionality as (C)
- Possible single-user local scenario management
Values
- Provides flexible what-if analysis, scenario management and scenario comparison that enable informed trade-offs between alternative solutions and conflicting business goals. (ps: CPLEX does not have this feature)
- Embeds the proven CPLEX Studio and DOC functionality into an IDE that allows the developer to work with them along with standard Java and others.
- Allows the development and deployment of optimization apps that are scaled to meet individual customers’ needs, from standalone Individual (desktop) configurations to enterprise configurations that allow collaboration between users while still solving locally to full enterprise solutions, with full collaboration and solving performed on a centralized server.
- Facilitates collaboration between planners with scenario sharing through a central repository.
- (OS, OE) Provides sophisticated optimization engines: CPLEX and CPO, to create smarter, resource-efficient plans and schedules.
- (C, P) Allows data analysis with drill-down and graphical display, enabling detailed visualization of data and decisions.
- (OS) Maximizes WebSphere Application Server for robust and scalable deployment, and BD2 for scenario management and sharing.
- (C, P) Allows the exchange of data between MS Word, Excel and other Office tools.
Benefits
- Scalable enterprise deployment
- Controlled relaxation of constraints: over-constrained problems are automatically relaxed during run time by CPLEX, which is careful to relax the fewest and least important constraints.
- Multiple objectives and goal programming
- Scenario management
- Collaborative Planning: shared Scenario Repository
- Division of corporate and planned data and processing: server-client architecture
- Modularity: custom GUI
- (C, P) Empowering business users: apps built with DOC help users to create, compare and understand planning or scheduling scenarios, adjusting any of the model inputs or goals and fully understanding the binding constraints, trade-offs, sensitivities and business options.
- (D) Slashing development costs
- (D) Refining optimization models
DOC with Uncertainty Toolkit
- also called IBM Research Uncertainty Toolkit
- Help business to resolve Challenges: large numbers of scenarios, complex mathematical models, …
- Guided uncertainty characterization (7 Steps)
- Automated formulation of uncertainty-aware decison model
- Trade-off analysis between robustness and cost effectiveness across multiple solutions / scenarios / KPIs simultaneously
- create , evaluate and select alternative solutions, including hedged against uncertainty through robust and stochastic optimization
- Create plans that anticipate the future
- Better quantify risk vs. reward
- increase margins
- reduce reactive changes
Integration & Architecture
1. Single (Local) Workstation Install

- External processes create input CSV files containing data to feed the optimization process.
- Planners receive input data file(s) via email, ftp, file share, …
- A Scenario database (open source Derby DB) is installed with each workstation. Drivers are included.
- Solves performed locally.
- DOC exports optimization results in CSV files or with custom work, in any other format.
Parts
- DOC Planner (one instance per user)
- DOC CPLEX Engine (one instance per user)
Pros
- No database connection required
- High control over work
- No servers required
Cons
- users work in isolation.
- Scenario sharing through Import/Export
- Computationally intensive solves tie up the workstation
- Requires high-end hardware configuration
- .odmapp files deployed to each workstation manually or via a scripted process
2. Hybrid Architecture

- The ideal low-cost solution
- Runs on Websphere Application Server (WAS) CE
- Requires connectivity to external DB (DB2, Oracle, SQL Server)
- Usually local routine perform ETL processes to bring data from external sources
- Solves performed locally
Parts used
- DOC Client (one instance per user)
- DOC CPLEX Engine (one instance per user)
- DOC Data Server (one instance, shared between applications)
- WAS Community Edition (CE)
Pros
- simple configuration
- low cost
- Scenario DB can be implemented in one of the client’s current database servers
- Users can share scenarios and collaborate on the planning process
Cons
- only support single solves per machine
- computationally intensive solves tie up the workstation
- requires high-end hardware configuration
3. Single Node Enterprise Architecture

- Multiple users collaborate on totally or partly shared scenarios (plans, schedules, …)
- Solves are performed remotely, using CPLEX Server
- Staging DB (recommended) houses (denormalized) data following the optimization data model. DOC will pick up the data from there to build Scenarios and process Solves.
- Number of concurrent Solves and data volume are the main requirements that influence hardware sizing.
- As of ODME 3.6, WAS CE (free Community Edition) is supported.
- IBM DB2 is included
Parts
- DOC Client (one instance per user)
- DOC CPLEX Server (one instance, shared between applications)
- Data Sever (one instance, shared between applications)
- WAS or WAS CE
Pros
- High performance.
- Processing work is offloaded to the Optimization server.
- Does not tie up workstation(s)
- Supports multiple, concurrent solves
- Users can share scenarios & collaborate on the planning process
- Mutualize license costs
Cons
- more complex solution
- requires high-end hardware for the CPLEX server
4. High Performance Multi-Node Architecture

Parts
- DOC Client (one instance per user)
- DOC CPLEX Server (multiple instances, shared between applications)
- Data Server (one instance, shared between applications)
- WebSphere Application Server Network Deployment (WAS ND)
Pros
- High performance.
- Solving work is offloaded to the processing nodes.
- Minimum waiting time
- Does not tie up workstation(s) while solving
- Supports multiple, concurrent solves
- Users can share scenarios & collaborate on the planning process
Cons
- Complex topology
- requires high-end hardware for the CPLEX servers
- higher cost
Summary: Parts Required
| Architecture | Planner | Client | CPLEX Engine | CPLEX Server | Data Server | Scenario DB | Application Server |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workstation | V | V | Derby | ||||
| Hybrid | V | V | V | DB2… | WAS CE | ||
| Enterprise Single Node | V | V | V | DB2… | WAS or WAS CE | ||
| Enterprise Multi-Node | V | V | V | DB2… | WAS ND |
Licensing Options
- How much DO do you need?
- DOC Developer: Number of named developers
- DOC Client: Number of named end-users accessing DOC applications; Potential alternative with web ui via REST
- DOC CPLEX Server:
- Number of concurrent optimization runs
- Number of cores (PVU) for one run #concurrent runs x #cores
- Amount of memory for one run #concurrent runs x memory for one run
- DOC Data Server
- How many concurrent users?
- How much data is stored in one scenario?
- How many scenarios?
More Details: Optimization Licensing & Configuration for IBM ILOG CPLEX & Decision Optimization Center